Python Main Method Tries to Run My Main Method Over and Over Again
Introduction Loops in Python
A concept in Python programming parcel that allows repetition of certain steps, or printing or execution of the similar ready of steps repetitively, based on the keyword that facilitates such functionality being used, and that steps specified under the keyword automatically indent accordingly is known equally loops in python. It is acting every bit a cake, with "while" continuing to execute until a certain specified condition is met and "for" executing till the index variable in the specified range of values reaches its final value.
Looping is a common miracle in any programming language; From a python perspective, the powerful programming linguistic communication offers two broad categories of loops.
They are as below:
- While Loops
- For loops
While Loops
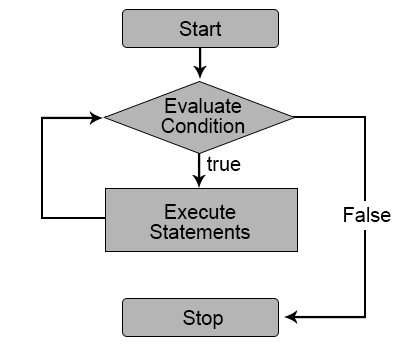
The common strategy behind while loops are they execute a set of statements until the given condition is satisfied. The next argument telephone call happens at the instance when the specified status is satisfied. The utilise of indented code segments determines the segment or the torso of the loop. Indentation starts the loop, and the line from which it starts to be unindented represents the end of the mentioned loop. All non-zero values are interpreted as truthful hither.
Flowchart
Example
Code
Code Snippet
north = 10 sum = 0 i = 1 while i <= due north: sum = sum + i i = i+1 print("The sum is", sum) While Loop Instance
Python Program for Matching a String
Import Section
- import string
- import random
- import time
Variable department
endeavourNext = '' completed = False iterator = 0 Propable Characters to Compare
propableCharacters = cord.ascii_lowercase + string.digits + string.ascii_uppercase + ' ., !?;:'
String to Be Generated
t = input("Enter the expected string or word : ")
Generate the Initial Random String
endeavourThis = ''.bring together(random.choice(propableCharacters)
for i in range(len(t)))
Iterate While Completed Is Simulated
Increment the iterator
iterator += 1 endeavourThis = endeavourNext fourth dimension.slumber(0.one) Driver Code
print("Target match constitute later " +
str(iterator) + " iterators")
For Loops
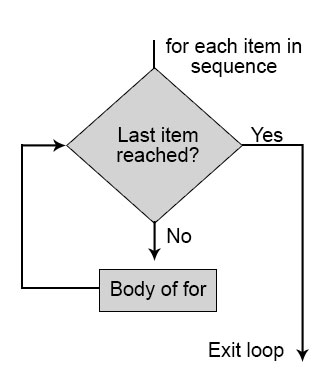
For traversing a sequential argument set, these loops are implied. The persistence of the loop is passed on pending the final item in the series is executed. While loop hither to the content of the loop is separated from the residue of the code by introducing the indentation. As like while loop hither to indentation plays an important role in determining the body of the loop involved. Indentation starts the loop, and the line from which it starts to be unindented represents the terminate of the mentioned loop.
Flowchart
Instance
for iterator_var in sequence:
statements(s)
Lawmaking Snippet
For Loop Instance#1
Python Program Using Turtle Graphing Technique
Import turtle
Office Definition
def border(obj1, panel_x, panel_y): obj1.penup() obj1.dwelling house() obj1.forward(panel_x / 2) obj1.right(90) obj1.forrard(panel_y / 2) obj1.setheading(180) obj1.pencolor('red') obj1.pendown() obj1.pensize(10) for distance in (panel_x, panel_y, panel_x, panel_y): obj1.frontward(altitude) obj1.right(xc) obj1.penup() obj1.dwelling() def foursquare(obj1, size, color): obj1.pencolor(color) obj1.pendown() for i in range(4): obj1.forwards(size) obj1.right(90) def primary(): panel = turtle.Screen() panel.title('Square Demo') panel_x, panel_y = panel.screensize() obj1 = turtle.Turtle() border(obj1, panel_x, panel_y) colors = ['ruby', 'orangish', 'yellow', 'green', 'bluish', 'violet'] obj1.pensize(three) for i, color in enumerate(colors): square(obj1, (panel_y / 2) / ten * (i+i), color) print('Hitting whatsoever key to exit') dummy = input() Main Programme Telephone call
if __name__ == '__main__':
chief()
For Loop Example#2
Programme to concatenate 2 LISTS into a dictionary.
Variable declaration
Key_elements=[] value_elements=[]
Count to exist processed
var1=int(input("Count of elements for the dictionry:"))
print (Key Elements)
for 10 in range(0,var1): chemical element=int(input("Element item entered" + str(x+one) + ":")) Key_elements.append(chemical element) Print (Value Elements)
for x in range(0,var1): element=int(input("Element item entered" + str(x+1) + ":")) value_elements.append(chemical element) d=dict(zip(Key_elements,value_elements)) #Impress Section print("The formulated dictionary is:") print(d) Nested loops
Nested looping is the process of looping i loop within the boundaries of others. So when the command flows from the outer loop to the inner loop, it returns back to the outer loop only when the inner loops are completed. Indentation is used to determine the body of the nested loops. Indentation starts the loop, and the line from which it starts to be unindented represents the end of the mentioned loop.
Example
Code:
for iterating_variable#1 in sequence#1:
for iterating_variable#2 in sequence#2:
statements(s)
statements(s)
while expression#one:
while expression#2:
statement(s)
statement(s)
Nested Loop Example
Python Programme for File Treatment
import os def listfile(types): current_path,filename = os.path.split up(os.path.abspath(__file__)) Nested Looping Department in The Program
Outer For Loop - - - - - - - - - -# for path,dir,file in os.walk(current_path): file_name = str(file) Inner For Loop
for type in types: if file_name.endswith(type): print(file_name) def deletefile(types): choice2 = input("Please enter the file to delete : ") os.remove(choice2) types = [".txt']",".srt]",".py]"] Header Area
impress(" = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = " ) print(" $$$$$$$$$$$$$ FILE HANDELING $$$$$$$$$$$$ ") print(" = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = ") File List
File_list = listfile(types)
File Operation
Print( Farewell Goodbye )
get out
else:
Print( Invalid Option )
exit
Python Loop Control Statements
Loops iterate higher up a block of code pending expression in testis simulated, but when at that place is an instance where we need to stop the loop without a cheque to the condition, that is where the loop control statements come up into play. The three major loop command statements in python are as below:
- Break: Terminates the loop and passes the control to the statement later on the loop. If a suspension is mentioned into a nested loop, then it is the innermost loop is where the break will initially cease.
- Continue: Skips the remaining sentences in the loop and checks the status posted in the loop.
- Pass: It just passes the execution when reaching a specific argument.
Loop Command Statements example
Python Programme Using Loop Control Statements
var_a = one var_b = two while var_a < var_b: print(" Code enters while loop ") var_c = ["SUV","sedan","hatchback","End"] for iterator in var_c: if iterator == "SUV": print("Hyundai creata") print("Mahindra bolero") impress("---------------") if iterator == "sedan": Loop Control Statement: Laissez passer
pass if iterator =="hatchback": print("Renault Kwid") impress("suzuki alto") impress("---------------") if iterator == "End": Loop Control Statement: Break
suspension
var_a = var_a+1
Benefits of python Loops: The fundamental advantages of loops are as beneath:
- Lawmaking reduction.
- Reduces code complication.
- Brings in more than stability into coding.
- Lawmaking redundancy is greatly resolved.
Determination – Loops in Python
The dominance exhibited past whatever programming language depends on the classified set of coding functionalities. In such instances, python programming'south looping structure is largely stable and flexible to code which stands out to be among the prior reasons which make this linguistic communication boss the market place.
Recommended Manufactures
This has been a guide to Loops in Python. Here we discuss what the Loops in Python are, While loops, and much more than with appropriate sample code. You tin also become through our other suggested manufactures to learn more –
- Python vs C++
- Python Collections
- Python File Operations
- Dictionary in Python
Source: https://www.educba.com/loops-in-python/
0 Response to "Python Main Method Tries to Run My Main Method Over and Over Again"
Post a Comment